Table of Contents
Offshore outsourcing has become an integral part of today’s global economy, playing a crucial role in driving efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling companies to focus on their core competencies. In this article, we will defineoffshore it outsourcing and discuss its importance in the context of the ever-evolving business landscape.
What is An Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing refers to the practice of contracting work to external service providers located in a different country. Companies often outsource non-core functions such as customer service, IT support, and back-office operations to offshore providers to leverage cost advantages, access specialized skills, and increase flexibility in their operations. By outsourcing these functions to countries with lower labour and operating costs, companies can achieve significant savings and improve competitiveness.
Importance of Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing has become a strategic imperative for businesses looking to remain competitive in an increasingly globalized market. By partnering with offshore outsourcing companies can access a vast talent pool of skilled professionals, many of whom have expertise in specialized areas that may need to be more readily available in their home country. This allows businesses to tap into diverse skills and capabilities, enabling them to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and accelerate growth.
Types of Offshore Outsourcing
There are several different types of offshore outsource, each serving a specific purpose and catering to various industry needs.
1) Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
Business Process Outsourcing, or BPO, involves contracting specific business processes to a third-party service provider. This type of outsourcing is commonly used for non-core functions such as customer service, human resources, finance and accounting, and procurement. By outsourcing these tasks to external vendors, businesses can focus on their core competencies and streamline operations to achieve greater efficiency.
2) Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO)
Information Technology Outsourcing, or ITO, involves delegating IT-related tasks and services to external service providers. This can include software development, network management, technical support, and data management. Outsourcing IT services can help businesses save costs on infrastructure, technology upgrades, and software licensing while gaining access to specialized expertise and resources.
3) Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)
Knowledge Process Outsourcing, or KPO, involves offshore outsourcing services high-level knowledge-based tasks requiring specialized skills and expertise. This can include market research, data analytics, financial analysis, and legal research. KPO services are typically used by finance, healthcare, and legal industries, where in-depth knowledge and analysis are critical for decision-making.
4) Legal Process Outsourcing (LPO)
Legal Process Outsourcing, or LPO, involves outsourcing legal services to external providers. This can include document review, contract drafting, intellectual property research, and litigation support. Law firms, corporate legal departments, and government agencies often utilize LPO services to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and access specialized legal expertise.

Benefits of Offshore Outsourcing
offshore outsource offers several advantages that can make a big difference for businesses. Here’s a look at some key benefits, including saving money, gaining access to specialized skills, and boosting efficiency.
Cost Savings
One of the biggest reasons businesses choose offshore bpo outsourcing is to save money. By outsourcing specific tasks, companies can avoid the high costs of hiring, training, and maintaining in-house staff. It’s also cheaper to tap into talent from countries with lower labour costs, which can lead to significant savings on overall expenses.
Access to Specialized Skills and Expertise
Another great benefit of offshore outsourcing is that it gives companies access to skills and expertise that might not be available locally. By working with bpo offshore providers, businesses can collaborate with professionals specializing in IT, finance, and marketing. This can improve the quality of products and services and even spark new ideas and innovations.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Outsourcing can also make a business more efficient and productive. When an external provider handles non-core tasks, the company can focus on what it does best. This streamlines operations speed up delivery times and improves overall performance. Plus, when experts handle specific tasks, the results are often better and faster, keeping customers happy and returning.
Challenges of Offshore Outsourcing
While offshore outsourcing has its perks, there are a few challenges that businesses need to be aware of. Let’s break down some of the common issues you might face.
Communication Barriers
One of the main hurdles is communication. Language differences, time zones, and cultural misunderstandings can sometimes occur when working with teams in different countries need to be clarified. This can lead to delays or mistakes. To avoid this, setting up clear communication channels and ensuring everyone understands what’s expected is essential.
Quality Control Issues
Another challenge is making sure the work meets your standards. When outsourcing, the quality of work might not always match what you’re used to, especially if the offshore provider has different practices. This can affect the final product or service. It’s essential to clearly outline your expectations and closely monitor the work to ensure it meets your quality standards.
Security Concerns
Security is also a big concern when outsourcing offshore. Sharing sensitive information with a partner in another country can be risky if their data protection practices differ from yours. To protect your data, choose a reliable partner, set up robust security measures, and ensure your contracts include strict confidentiality terms.
Common Industries That Utilize Offshore Outsourcing
While various industries benefit from offshore outsourcing, three of the most common industries that utilize this practice include information technology, customer service, and manufacturing.
a) Information Technology
The information technology industry is one of the largest sectors relying heavily on offshore outsourcing. Companies often outsource software development, web development, and IT support to offshore locations where skilled professionals can provide high-quality services at a lower cost. By outsourcing IT services, companies can access specialized skills and expertise that may not be available locally, allowing them to innovate and stay ahead of the competition.
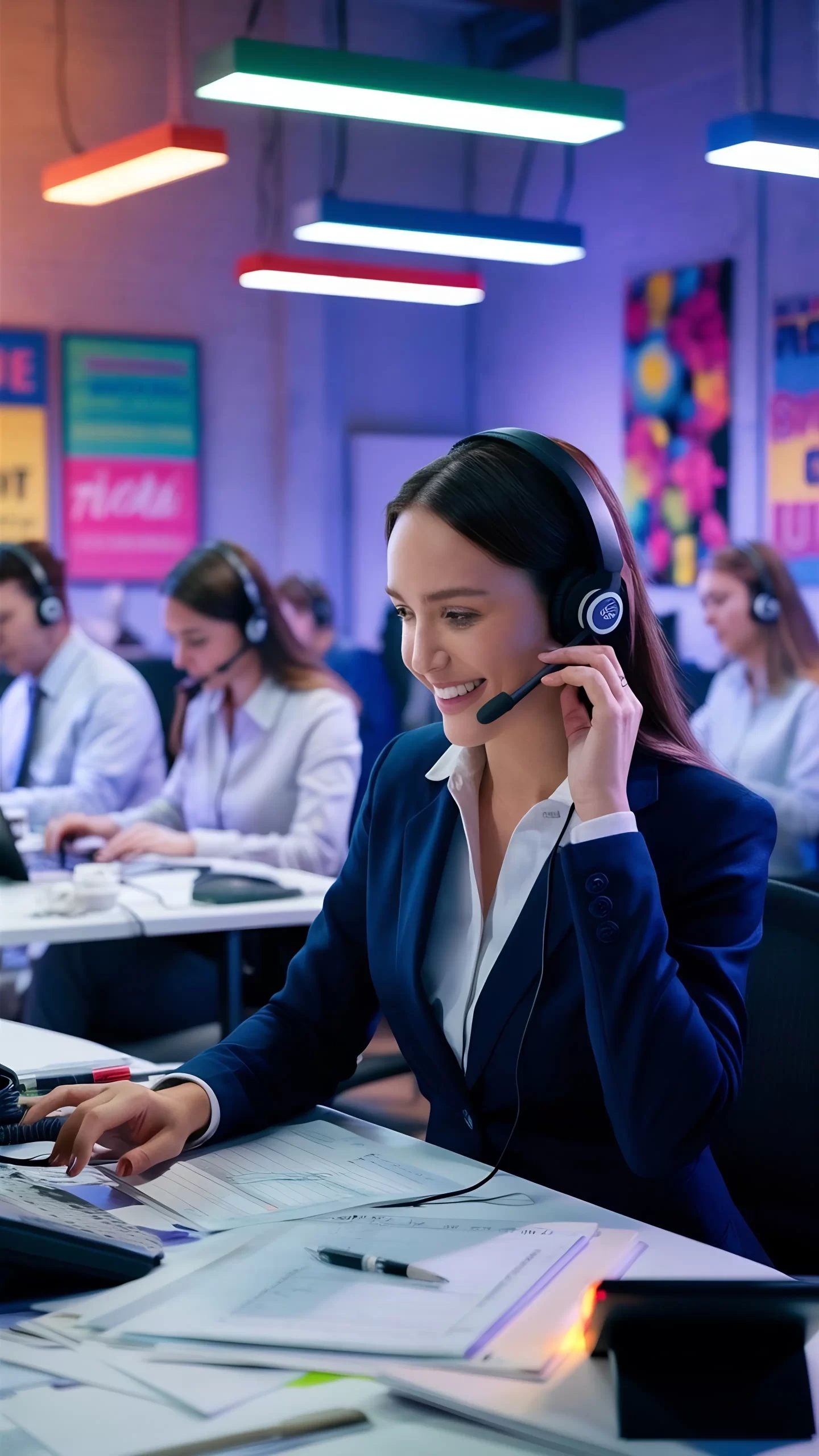
b) Customer Service
Customer service is another industry that frequently utilizes offshore outsourcing to enhance operations and provide round-the-clock customer support. Companies outsource call centre operations and technical support services to offshore locations where agents can assist customers in multiple time zones, ensuring customer queries are promptly addressed. By outsourcing customer service, companies can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty while reducing operational costs.
c) Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has also embraced offshore outsourcing as a strategic business practice to maximize efficiency and reduce production costs. Companies often outsource manufacturing processes such as assembly, fabrication, and packaging to offshore locations with lower labour costs. By outsourcing manufacturing, companies can focus on core business activities, minimize turnaround times, and achieve economies of scale to meet the demands of a global market.
What Is Offshore Outsourcing?
Offshore outsourcing plays a critical role in today’s global economy, enabling companies to achieve cost savings, access specialized talent, expand their international footprint, and stay agile in the face of evolving market dynamics. By leveraging offshore outsourcing, businesses can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.